
Proof-of-Stake (PoS): A Revolutionary Shift in Blockchain

Most cryptocurrencies circulating in the market rely on blockchain technology as the foundation for facilitating transactions. These transactions are verified using a system called a consensus mechanism. The two most popular consensus mechanisms today are Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS). PoW, used by Bitcoin’s blockchain, is designed to prioritize asset transfer security. As cryptocurrency has evolved, the PoS system was created, offering a more environmentally friendly consensus mechanism that doesn’t consume as much energy as PoW. So, what is the Proof-of-Stake system? Why are more blockchains adopting the PoS system? This article will comprehensively explain the PoS mechanism.
Article Summary
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism that ensures only valid transactions are added to blocks on the blockchain by requiring validators to lock up their cryptocurrency to secure the network.
PoS makes blockchain transactions more environmentally friendly and allows users to earn passive income through staking.
Crypto assets with PoS can process transactions quickly and cheaply, solving scalability issues for crypto assets aiming to create a decentralized application ecosystem.
Definition of Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
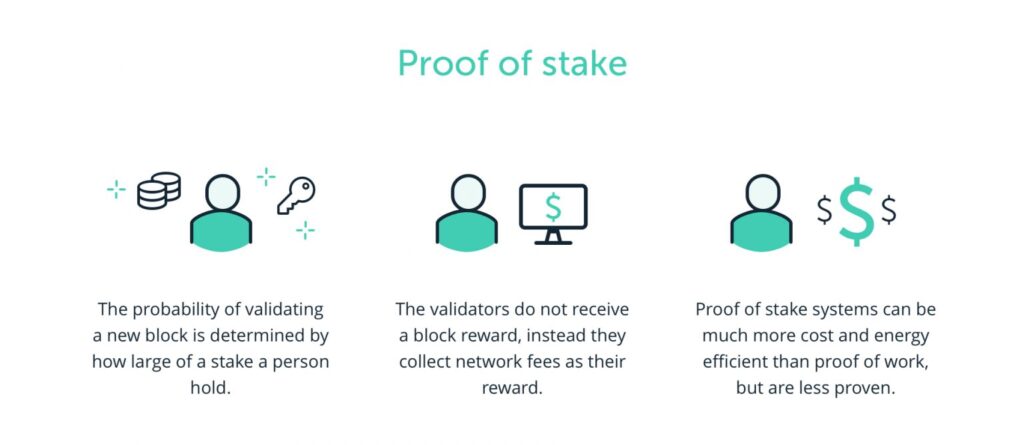
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is an algorithm for achieving consensus that requires users (validators) to stake a certain amount of tokens to have the opportunity to verify transactions and earn rewards. In short, this algorithm relies on the number of tokens a user holds in the system and selects transaction validators on the blockchain based on this.
This complex mechanism is implemented to achieve distributed consensus, a state where the system runs securely and decentralized because transaction verification is done by other users. In the PoS system, there are no miners racing to use their computing power to process transactions and earn rewards.
Creating new blocks in the PoS mechanism is done randomly yet systematically, consuming much less electricity. This makes it more environmentally friendly than PoW. Additionally, in the PoS system, anyone can become a transaction validator as long as they have a certain amount of tokens and meet some requirements.
How Does Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Work?
3 pillars of the Proof-of-Stake system characteristics. Source: Ledger
The Proof-of-Stake system does not rely on mining to create new blocks, so it is not called ‘mined’ but ‘minted’ or ‘forged’. Instead of mining new blocks through computational work, the PoS system requires users to demonstrate ownership of a certain amount of crypto assets.
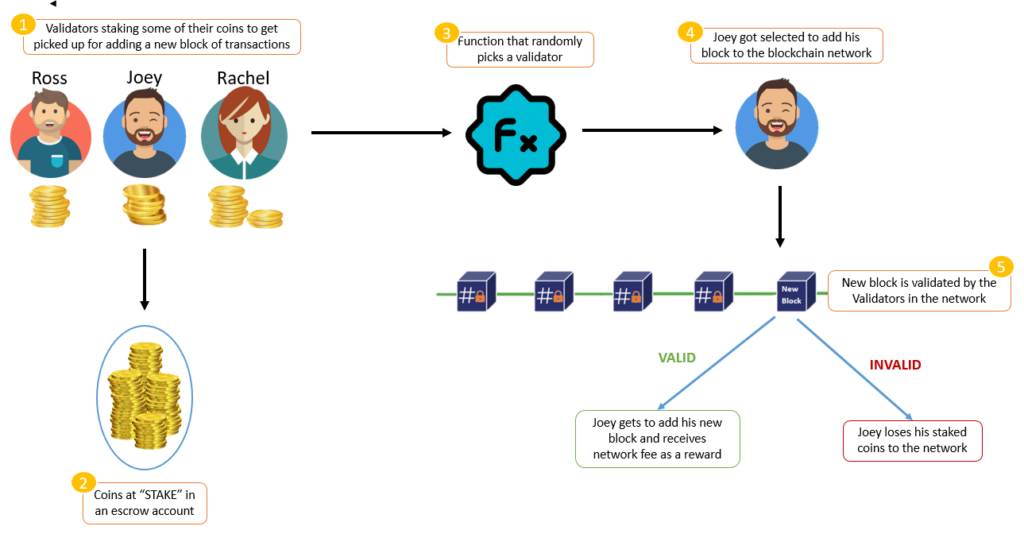
In the PoS method, miners are called ‘validators’ who stake their tokens to participate in transaction verification. Tokens staked in the system are held as collateral as long as the user remains a validator. When a validator is selected, their role is to verify the validity of transactions in the block, sign them, and register the new block on the network for validation.
Selecting Proof-of-Stake Validators
PoS validators are chosen randomly but prioritize those with higher stakes. The more crypto assets staked, the higher the chance of being selected as a validator. However, the algorithm will still randomize validator selection to avoid attacks from hackers by ensuring that those with the highest stake are not always chosen.
One key difference between PoS and PoW systems is the reward given to transaction validators. Most PoS blockchains have already created their entire supply of crypto assets at the start. Therefore, rewards in the PoS system are given in transaction fees, not new crypto assets like Bitcoin. However, there are exceptions where PoS crypto assets still provide new coins as staking rewards.
Validators are rewarded when they validate transactions and register new blocks. If a validator fails to perform their task, a certain number of staked tokens will be forfeited, and they cannot be a validator for a certain period.
Source: Naukri Learning
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)
Users who want to participate in the verification process but cannot be validators can choose to be ‘delegators’. Delegators are ordinary users who stake their crypto assets with validators to earn rewards. This delegation or staking system is used in Delegated Proof-of-Stake, an advancement of the PoS method.
Differences Between Proof-of-Stake and Proof-of-Work
As explained, technically and operationally, Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake systems are very different. Fundamentally, both have the same goal: to create a decentralized, secure system without relying on third parties. Additionally, PoW and PoS capabilities are very different, especially concerning scalability and handling network congestion.
Ethereum, one of the first smart contract platforms, initially used a PoW system and often faced scalability issues, making transaction costs very high. This happened because the PoW system’s transaction verification method is very complex and requires significant computing power. This issue does not occur in PoS blockchains because its verification method does not use large computational power.
However, on September 15, 2022, Ethereum made a significant change to its network by transitioning from PoW to PoS. This change is known as The Merge Ethereum.
| Functionality | Proof-of-Stake | Proof-of-Work |
|---|---|---|
| ⚡ Energy Consumption | Low | High |
| 🛡 Security | Not yet proven as it is relatively new | Secure and well-tested |
| 🔧 Decentralization vs Centralization | More decentralized due to an unlimited number of validators | More centralized due to mining companies |
| 🧑💻 User Staking | Possible | Not possible |
| ⛏ Validator/Miner Requirements | Tokens with a certain amount | Electricity power and mining computers |
| ⚙ Scalability | High due to simple transaction verification methods | Low due to complex and difficult transaction verification methods |
Advantages of PoS Over PoW
🍀 Environmentally Friendly: PoS consumes much less electricity and is more eco-friendly than PoW.
🏎️ Transaction Speed and Cost: The simple and easy PoS verification method facilitates a fast blockchain network without high transaction costs.
💸 Staking Opportunities: PoS blockchains can involve users in staking to earn passive income.
👨💻 Scalability for App Developers: Crypto app developers prefer to build their applications on PoS blockchains so users do not have to pay high transaction fees.
Some Coins Using PoS System
Solana (SOL)
Solana is a cryptocurrency that uses a PoS verification system combined with Solana’s proof-of-history algorithm. Proof-of-history adds timestamps to all transaction validation processes. These two verification systems work together to create a blockchain that can process transactions quickly and at low costs.
Additionally, Solana innovates further on these verification systems by adding the Gulf Stream protocol at the PoS level to reduce transaction validation duration. Currently, Solana is one of the fastest blockchains with an application ecosystem that rivals Ethereum.
Cardano (ADA)
Cardano is a cryptocurrency using a modified proof-of-stake method called the Ouroboros system. Ouroboros is a PoS modification that utilizes time partitioning to separate the validator selection process. This time partitioning is called an epoch, divided into several slots. Each slot has a slot leader who acts as a validator.
Cardano’s PoS system modification ensures each validator validates transactions for a predetermined time (an epoch usually lasts several days). This selection is done randomly and alternates, so validators change every epoch.
Fantom (FTM)
Fantom is a crypto asset that uses a modified PoS method created by Fantom. This modification creates a leaderless proof-of-stake called Lachesis. Lachesis uses directed acyclic graph (DAG) technology to structure the transaction sequence for each validator. Lachesis allows each validator to validate transactions without waiting for confirmations from other validators. Thanks to this system, the Fantom network only takes 1-2 seconds to verify and validate transactions.
Final Thoughts
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, Proof-of-Stake (PoS) has emerged as a superior alternative to Proof-of-Work (PoW). With its energy-efficient model, low fees, and scalability, PoS is rapidly becoming the preferred choice for cryptocurrency networks and decentralized applications.
With major projects like Ethereum, Solana, Cardano, and Fantom utilizing PoS, it’s clear that this mechanism represents the future of blockchain technology. Whether you’re a crypto investor looking for staking opportunities or a developer building DApps, PoS provides a more sustainable and efficient ecosystem for blockchain innovation.
Learn more knowledge of crypto through various articles on Safubit Academy. All articles on Safubit Academy are created for educational and informational purposes only and are not intended as financial advice.
Don’t forget to follow our social media:
X : https://x.com/safubit
Medium : https://medium.com/@safubit.exchange


 February 4, 2025
February 4, 2025