
DAOs Exposed: Unlocking New Paths To Wealth & Governance

One of the most significant technological advancements since the emergence of cryptocurrency is the concept of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). A DAO is an internet-based organization that operates without centralized leadership, where governance decisions are made through community voting in a transparent and decentralized manner.
Unlike traditional organizations, DAOs do not have a hierarchical management structure. Instead, every decision is proposed and approved by members collectively, and transactions are automated through smart contracts recorded on the blockchain.
DAOs can be used in decentralized finance (DeFi), social initiatives, charity, and governance systems. This article explores what DAOs are, how they function, and their real-world applications.
Article Summary
💡 Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAO) are entities without centralized leadership. DAOs operate without hierarchical management and are governed by a community organized within a set of rules enforced on the blockchain.
🔗 Transactions and financial rules in DAOs are recorded on the blockchain. This eliminates the need for third parties in financial transactions, simplifying them through smart contracts.
👛 One example of DAO application is in fundraising and charity. Without centralized leadership, charitable organizations can receive donations from anyone around the world, and everything can be run automatically and transparently.
📊 As of July 2022, there are more than 3.8 million governance token holders in nearly 4,800 DAO organizations, according to data from DeepDAO. Across these organizations, there is over $8.8 billion stored in DAO treasuries, down $1.2 billion from the previous month.
What Is a DAO?
Have you ever imagined an organization run transparently and decentralized, with all decisions made based on member voting? With all organizational funds managed transparently and based on stakeholder approval? This can be achieved with a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO).
A Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) is essentially an entity without central leadership, where decisions are made from the bottom up and governed by a community organized within a set of rules written on the blockchain. With a DAO, all organizational governance, including fund management, can be based on collective and transparent decisions since everything is recorded on the blockchain for joint monitoring by members and stakeholders.
The difference from traditional organizations or businesses is that no one has absolute authority without the group’s consent. Decisions are governed by proposals and voting to ensure that everyone in the organization has a voice.
Thus, there are no CEOs who can authorize expenditures based on their own desires, and there is no possibility of manipulating the books. Everything is open, and rules regarding expenditures are embedded into the DAO through its code.
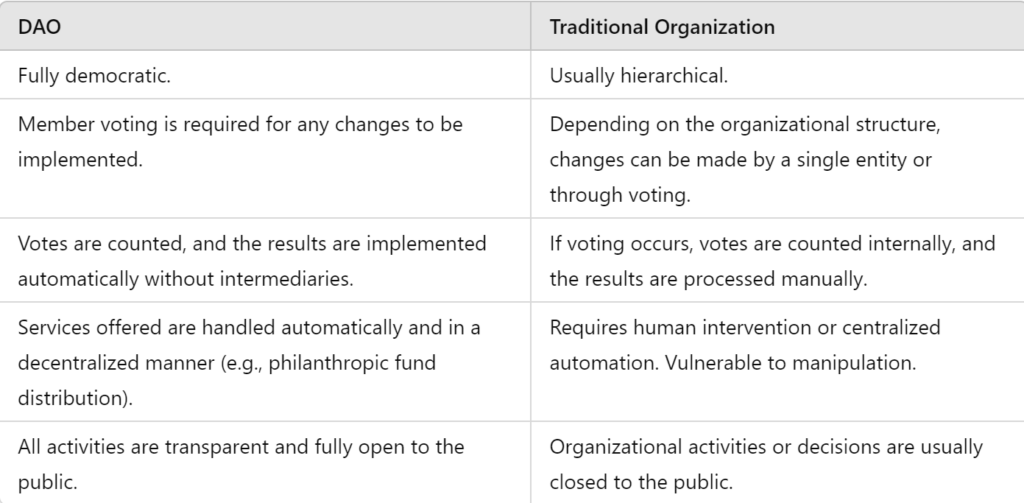
Differences Between DAO and Traditional Organizations
As previously explained, unlike traditional organizations or companies, every decision in a DAO is made based on voting by its members, conducted automatically, transparently, and in a decentralized manner. Here is a more detailed explanation, quoted from Ethereum.org.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)

Some decentralized finance platforms, such as Uniswap and AAVE, issue governance tokens that provide voting rights to their communities to run and develop the projects. For example, anyone holding UNI tokens can vote or delegate their vote on development proposals that can alter the operations or infrastructure of the Uniswap protocol.
Charity and Fundraising
By running a DAO for charity or fundraising, you can receive memberships and donations from anyone in the world, and the group behind the organization can decide how they want to spend the donations. Everything can be run automatically and transparently.
How Does DAO Work?
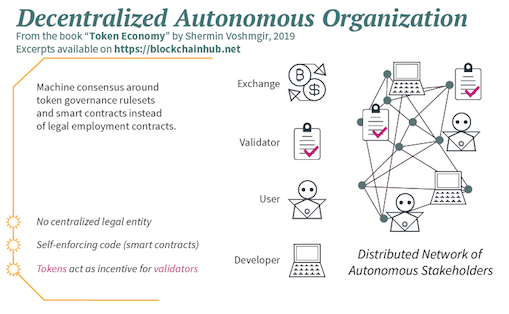
Source: https://blockchainhub.net/dao-decentralized-autonomous-organization/
Decentralized applications like DAOs are built using smart contracts. Smart contracts define and execute organizational rules and treasury operations automatically. Once the contract is active on the blockchain, no one can alter the rules except through voting. If someone tries to perform actions not covered by the rules and logic in the code, the attempt will fail.
And since the treasury is also governed by smart contracts, it means no one can spend the organization’s funds without the group’s consent. DAOs ensure that the organization operates transparently. Members make decisions collectively, and fund usage is carried out automatically and sanctioned when votes are approved.
After establishing the rules recorded on the blockchain, the next step is to ensure funding for the organization’s operations and determine the governance mechanism. This is usually achieved through issuing tokens, where the protocol sells tokens to raise funds and fill the DAO’s treasury.
In return for the funds provided through token purchases, token holders are given certain voting rights, usually proportional to the amount of tokens they hold. Once funding is complete, the DAO is ready to operate.
Examples of DAO Implementation and Governance Tokens
Referring to the way governance tokens work and are implemented on Uniswap, the governance process begins in the Governance Forum, where you can find proposals under consideration, gather information about community sentiment, and engage with the community. Below is an example.
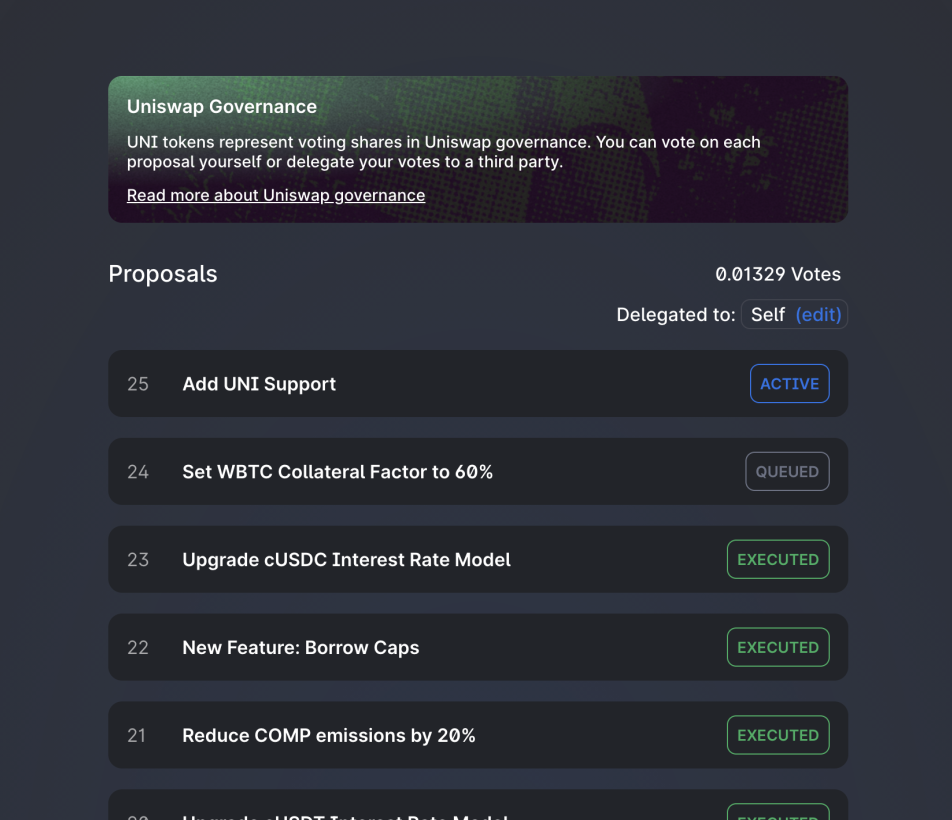
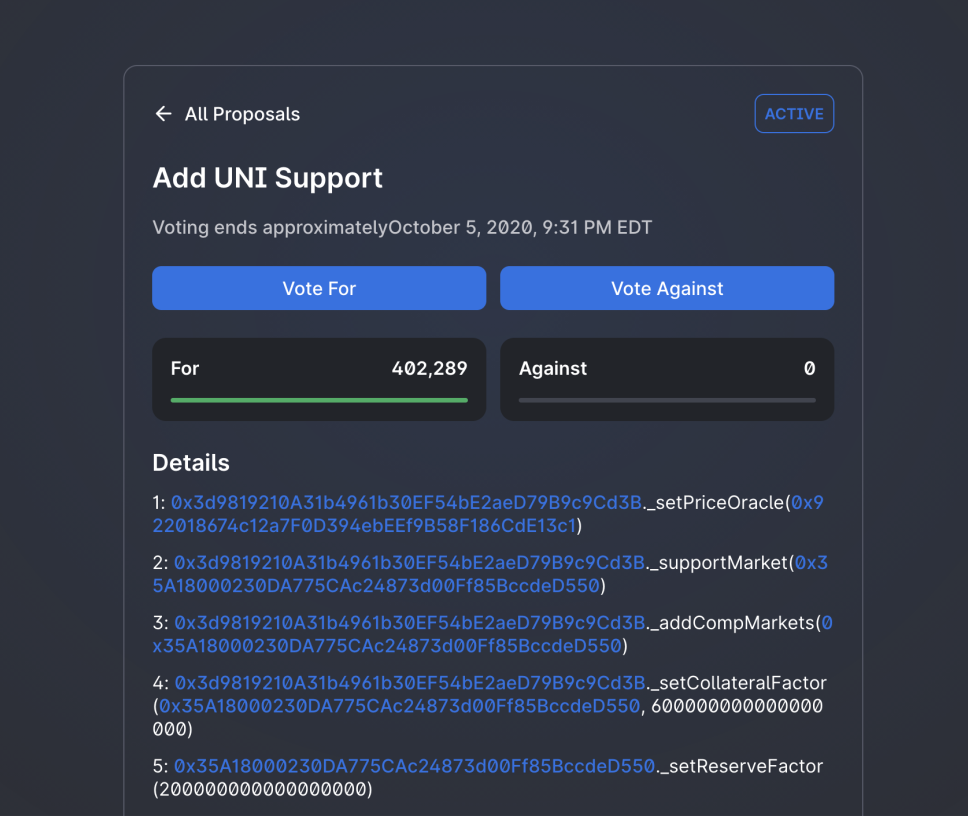
After a proposal successfully passes the proposal process and is ready for voting, it will appear on the Uniswap voting dashboard – where you can see all current and past Uniswap proposals.
If the proposal is active for voting, it will show “active” next to the proposal title. By clicking on the proposal, you can access all the necessary information, documentation, and discussions needed for voters to make an informed decision.
What Are the Drawbacks of DAOs?
As internet-based organizations, DAOs have several advantages over traditional organizations. These advantages include minimal trust needed between parties and the absence of a hierarchical structure, allowing innovative ideas from the community to be considered by all members of the organization.
However, despite these advantages and innovations, DAOs are not without their drawbacks. Here are some disadvantages of DAOs compared to traditional organizations:
👨💻 No Authority Figure: Without a clear authority figure or chain of command, decentralized organizations may operate more slowly because decision-making takes longer.
💥 Possibility of Disagreements: When the community is highly divided, it can split the organization into two factions.
🚧 Lack of Change: In some DAO projects, those with the most tokens can take over or dominate decision-making. Thus, governance can resemble traditional organizations.
Conclusion
DAOs are reshaping the future of organizational governance by eliminating centralized control and enabling transparent, community-driven decision-making.
✔ Smart contracts ensure trustless automation.
✔ Governance tokens empower stakeholders.
✔ Blockchain transparency enhances accountability.
Despite challenges in governance efficiency and security, DAOs continue to gain traction in DeFi, social initiatives, and corporate governance models.
Learn more knowledge of crypto through various articles on Safubit Academy. All articles on Safubit Academy are created for educational and informational purposes only and are not intended as financial advice.
Don’t forget to follow our social media:
X : https://x.com/safubit
Medium : https://medium.com/@safubit.exchange


 February 5, 2025
February 5, 2025