
What Happened to Ethereum After The Merge?

Ethereum successfully transitioned from a proof-of-work (PoW) to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism on September 15, 2022, in an event known as The Merge. This historic upgrade was anticipated by the crypto community for years and was one of the most significant developments in Ethereum’s history.
Beyond drastically reducing energy consumption, The Merge was expected to positively impact Ethereum’s long-term value, potentially making ETH deflationary. But what exactly changed after The Merge? How did it affect Ethereum’s supply, price, miners, and institutional interest? Let’s dive into the post-Merge updates.
Article Summary
🔗 By changing its system from PoW to PoS, Ethereum’s energy consumption has decreased by 99.95%, making it an environmentally friendly blockchain.
⛽️ The issuance rate of new Ether (ETH) has decreased after The Merge. However, gas fee burning has also decreased due to a drop in transaction volume on the Ethereum network amid the current bear market. This has led to an increase in ETH supply after The Merge.
📉 With the continued increase in ETH supply in the current market, ETH has not yet become a deflationary asset. As of the writing of this article (September 23, 2022), the price of ETH stands at $1,357, down about 17% in five days from $1,636.
What Happened to Ethereum After The Merge Was Successful?
Ethereum Becomes a Green Blockchain
One of the biggest criticisms of the growing adoption of crypto is its negative impact on the environment. This is because the process of issuing assets for early-generation cryptocurrencies like Ethereum (ETH) used a proof-of-work (PoW) system, which required specialized computers and consumed vast amounts of energy.
By switching to a proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanism, Ethereum’s energy consumption has been reduced by 99.95%. Thus, The Merge has made Ethereum environmentally friendly, or a green blockchain.
The energy required to create blocks on the Ethereum network is now equivalent to the energy usage of a typical laptop for each node, amounting to 0.01 TWh/year.
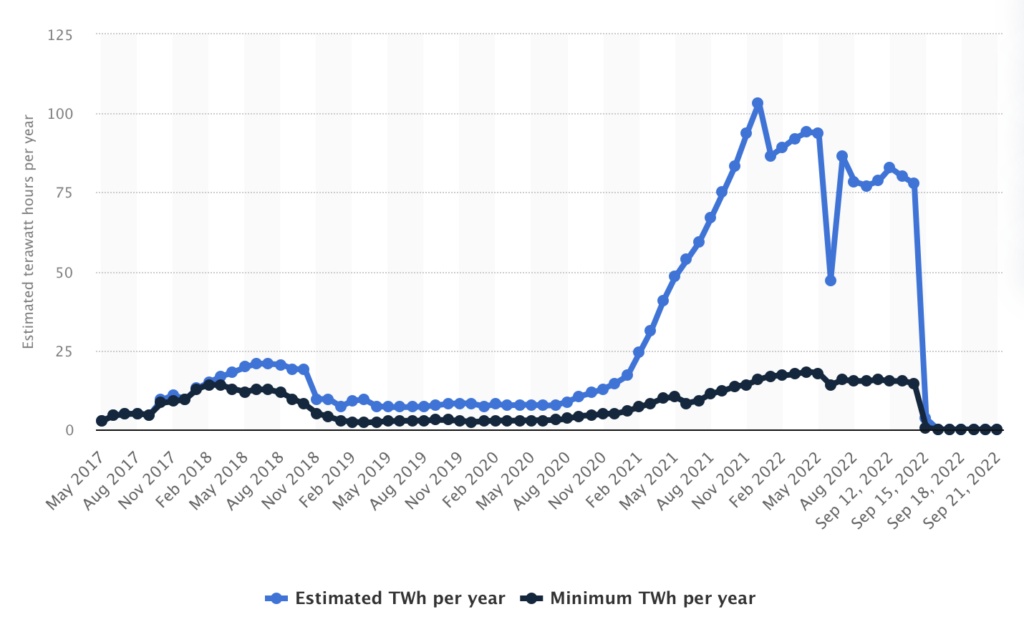
Global Ethereum Energy Consumption from May 2017 to September 22, 2022. Source: Statista
According to the Statista chart above, energy consumption used by Ethereum to operate its blockchain mechanism sharply decreased on September 15, 2022, when The Merge was implemented, to 0.6 TWh/year, and further to 0.01 TWh/year on September 16, 2022. This represents a positive environmental impact of The Merge for the crypto world.
Decrease in New ETH Issuance
Before The Merge, new ETH issuance was awarded to miners who secured the network and processed transactions. The daily issuance of ETH as rewards for miners in the PoW system was around 13,000 ETH, or approximately 4,931,000 ETH per year. Most of them then sold these rewards to cover operational costs like electricity. This cycle contributed to inflation and selling pressure on ETH.
The Ethereum mining system has now been replaced by the PoS mechanism. New ETH is issued as rewards to validators who secure the network and process transactions. However, the reward numbers for validators are much smaller than what miners used to receive. As of September 23, 2022, data from the UltraSound Money site indicates that only 603,000 ETH will be issued annually, or about 1,600 per day.
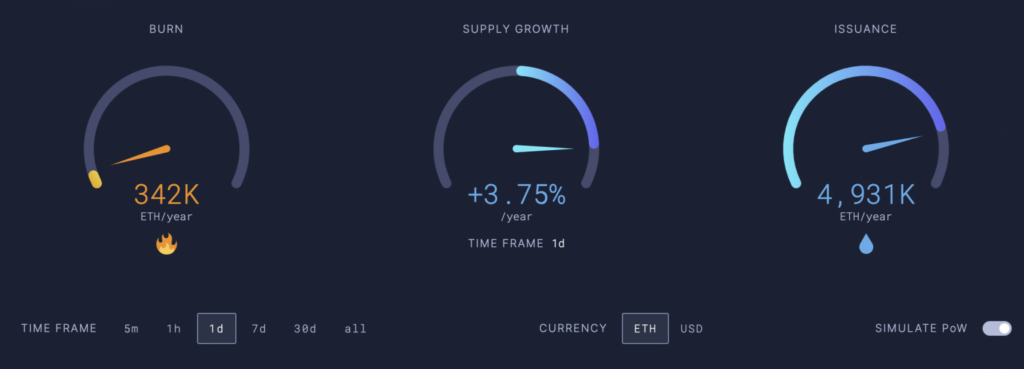
Burn rate, supply growth, and the amount of ETH issued by Ethereum before the Merge. Data from September 20, 2022, from Ultrasound Money.
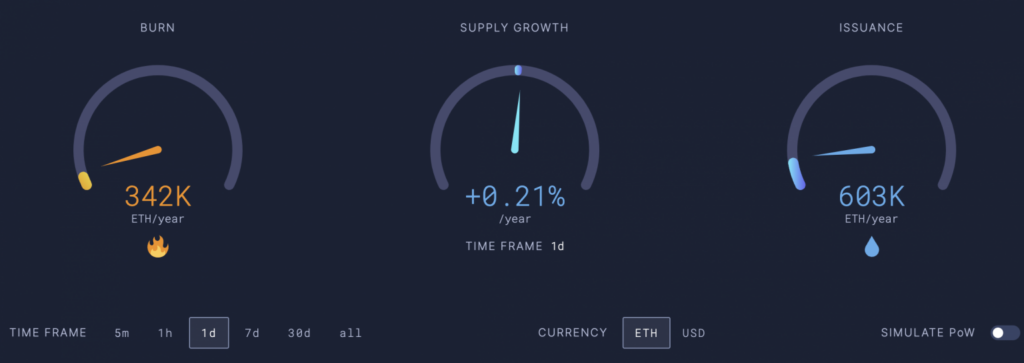
Burn rate, supply growth, and the amount of ETH issued after The Merge. Data from September 20, 2022, by Ultrasound Money.
The chart above shows the comparison of new ETH issuance before and after The Merge. If we calculate, 603k is 12% of 4931k (the ETH issuance number before The Merge), meaning the issuance of ETH has decreased by about 88% from before. However, the numbers for new ETH issuance and supply growth are not stable and change based on factors like staking rewards percentage and network activity.
Additionally, in August 2021, Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP)-1559 was implemented. This upgrade burns a portion of the gas fees from each transaction to reduce the circulating ETH supply. The amount of gas fees burned depends on network activity. The EIP-1559 mechanism burned around 35,315 ETH in the last month, or about 1,100 per day.
However, this amount has not been able to offset the new ETH issuance rate post-The Merge (1,600 ETH). As seen in the chart below, ETH burning has significantly decreased since 2021. This is due to the reduction in transactions on the network amid the 2022 bear market.
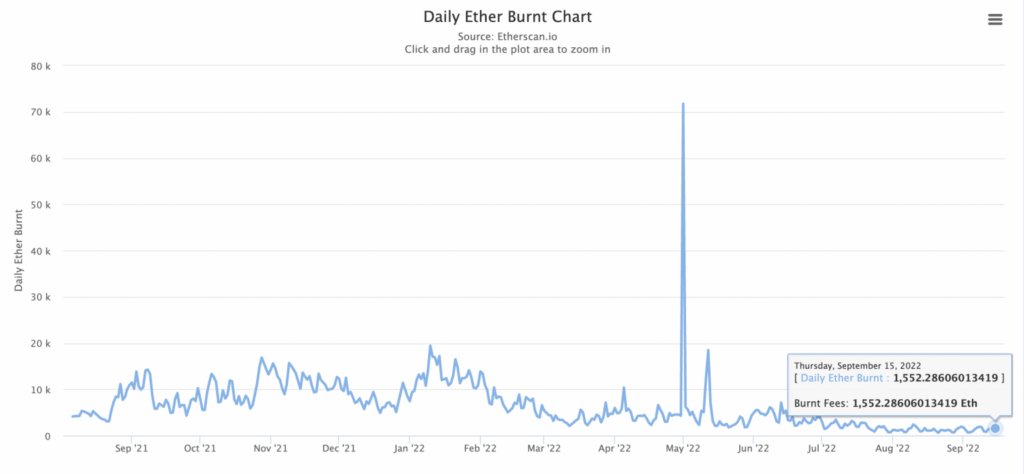
ETH burning per day. Source: Etherscan.io
The Merge was previously projected to make ETH a deflationary asset. This is because new ETH issuance would decrease significantly with the elimination of rewards for miners. Does this mean ETH will become a scarcer and more valuable asset? This may happen. However, despite the reduced supply, gas fee burning has also decreased along with the drop in transactions on Ethereum.
In fact, 8 days after The Merge (September 23, 2022), the ETH supply actually increased by around 4,736. The amount of new ETH also exceeded the ETH burned from gas fees. This is due to the declining demand for Ethereum usage because of the bear market. In the long run, the decrease in ETH issuance and burning could have positive effects.

Changes in ETH supply since the Merge
ETH Staking as a Result of The Merge
In the staking system, anyone can participate as a validator. However, you need at least 32 ETH and specific software to function as a validator. For ETH holders who want to participate in staking but do not meet the minimum amount, there is an option to delegate ETH to a validator pool. You will receive a percentage of rewards in ETH, the amount agreed upon with the validator.
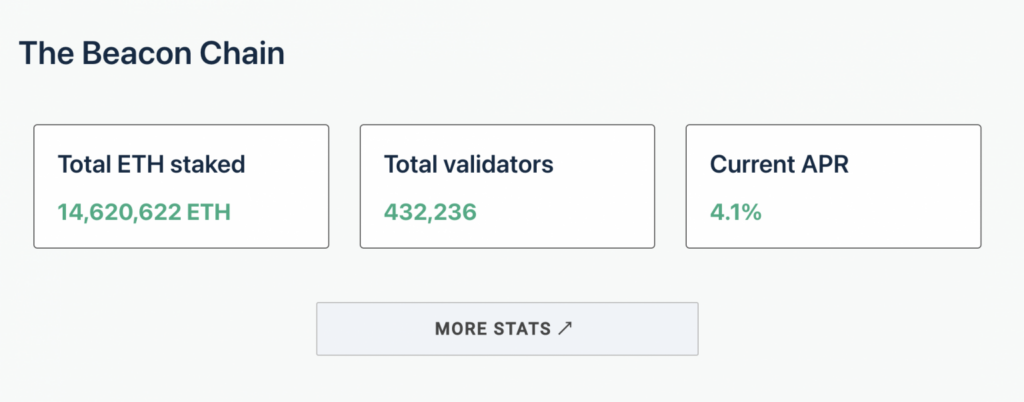
Source: Ethereum Launchpad
As of September 23, the total ETH staked is 14,620,622 ETH with 432,236 validators. Validators earn an interest rate of 4.1% APR (Annual Percentage Rate) for their roles.
After The Merge, validators will earn income from gas tips previously given to miners. From these tips, validators might receive twice the APR amount.
According to data from Nansen on September 13, 2022, only 11.3% of the total ETH supply is in staking, much less than MATIC (41%) and SOL (77%). This is influenced by several factors including the high minimum ETH required to become a validator (32 ETH), the staking system that does not allow users to directly withdraw ETH, and the small percentage of rewards.
The current ETH staking system does not allow users to unstake (unlock their assets). Investors who locked ETH for staking will only be able to unstake when the Shanghai fork is implemented in 2023. When stakers can withdraw, it is still unknown, and the amount of ETH that can be withdrawn will also be limited per day. It is estimated that around 30 million ETH will enter the market when the unstake feature is applied during the Shanghai fork.
Ethereum Miners Switching to Other Networks
After Ethereum successfully transitioned its network to Proof-of-Stake (PoS), the presence of miners is no longer needed. This is one of the most significant impacts of The Merge on Ethereum. The validation of transactions and network security is now entirely done by validators using the staking system. This makes mining rigs useless on the Ethereum network.
To continue running mining rigs, miners are expected to switch to other altcoins like ETHW, ETC (Ethereum Classic), and RVN (Ravencoin) by making some modifications to their mining systems. However, the profits obtained are far below those when mining ETH.
According to data from Minerstat quoted by Coindesk on September 16, 2022, the reward for mining a block of Ethereum Classic about 24 hours ago was ETC 0.0186484, or about 70 cents, but in the last hour, it dropped to ETC 0.00030658, or about 11 cents. Similarly, RVN miners who received RVN 30.28478584, or $1.77 per block 24 hours ago, saw it drop to RVN 0.82968431, or about 5 cents in the last hour.
This decline is attributed to many ETH miners switching to mine ETC, increasing the hashrate, which results in higher difficulty and reduced rewards for mining a block.
Concerns About Ethereum Becoming More Centralized
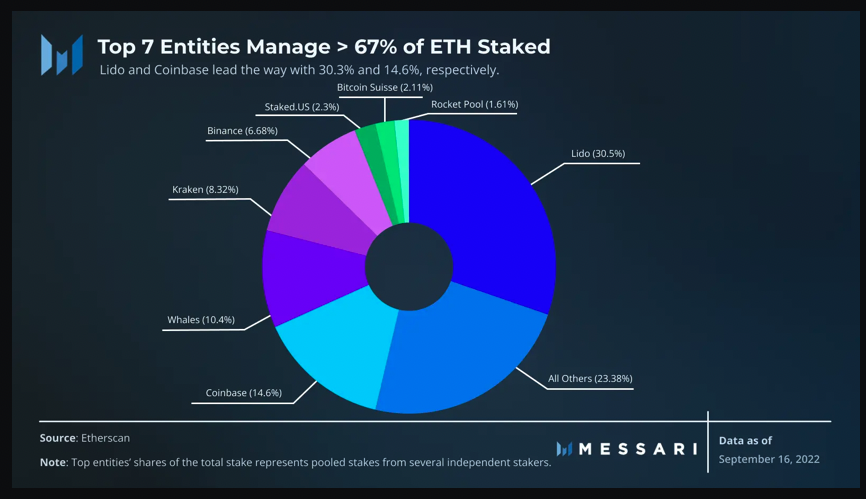
A company that acts as a validator on Ethereum.
The PoS system was supposed to make Ethereum more decentralized since anyone worldwide could participate as a validator. However, on September 15, Martin Köppelmann from Gnosis, an Ethereum-based infrastructure company, reported that of the 1,000 blocks created, 420 blocks were made by Lido and Coinbase.
Lido is a liquidity provider platform for Ethereum staking, and Coinbase is the third-largest cryptocurrency exchange in the world. These two platforms each control 30.5% and 14.6% of the Ethereum staking network, respectively.
As mentioned before, to become a validator, users must stake 32 ETH and run specific software considered quite complex. Therefore, many users entrust their ETH to Lido, Coinbase, and other staking groups to earn rewards without being full-time validators.
If a single entity controls 66% of the Ethereum staking network, it becomes increasingly difficult for smaller validators to participate. Additionally, centralized security among a few entities increases security risks for the network. The argument that Proof-of-Stake makes Ethereum more decentralized appears to be in question. Current validator data suggests that the changes in Ethereum may have made it more centralized.
Impact of The Merge on Institutional Confidence in Ethereum
Ethereum is currently the most widely used blockchain with smart contracts. The Ethereum network is used by nearly 60% of DeFi (Decentralized Finance) platforms such as MakerDAO, Uniswap, Aave, Curve, and others. As of September 2022, the entire DeFi ecosystem is valued at $53.86 billion, with Ethereum contributing about 57% of the total value locked (TVL) at $30.8 billion.
In the past two years, several financial institutions have started entering the DeFi and Web3 ecosystem to develop their business models, such as Goldman Sachs and Barclays, as well as retail banks Banco Santander and Itau Unibanco.
By implementing the Proof-of-Stake system, Ethereum has become an environmentally friendly blockchain. The Merge update provides an opportunity for institutional investors who consider Ethereum’s environmental impact to start investing.
These are some of the changes and impacts of The Merge on Ethereum that we have summarized for you as educational material to understand the technological developments occurring in the Ethereum blockchain.
Learn more knowledge of crypto through various articles on Safubit Academy. All articles on Safubit Academy are created for educational and informational purposes only and are not intended as financial advice.
Don’t forget to follow our social media:
X : https://x.com/safubit
Medium : https://medium.com/@safubit.exchange


 February 7, 2025
February 7, 2025