
Blockchain Trilemma Explained: The Big Challenge of Crypto

The blockchain trilemma is a problem faced by decentralized platforms today, where each blockchain can only focus on 2 of its 3 main strengths: decentralization, security, and scalability. This means that development teams are faced with the choice of sacrificing one of these three aspects. So, what is the current state of the blockchain trilemma? Are there any solutions to this problem? Find out in the detailed review in the following article.
Article Summary
- ⚠️ The blockchain trilemma is a problem where development teams must sacrifice one aspect of decentralization, security, or scalability.
- 🚧 Scalability is currently a focus for development teams to broaden blockchain adoption.
- 🔗 The presence of technologies like layer-1 and layer-2 has so far been the most effective way to optimize a blockchain’s scalability.
What is the Blockchain Trilemma?
In building a blockchain, there are three main aspects considered by development teams: decentralization, security, and scalability. Ideally, a blockchain could maximize all three aspects. However, in practice, development teams are faced with the choice to “sacrifice” one aspect to maximize the other two. This dilemma, or trilemma, is what is known as the blockchain trilemma. Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin popularized the concept of the blockchain trilemma.
Aspects of the Blockchain Trilemma
Decentralization
Decentralization is a concept that ensures the blockchain system does not rely on a single controlling entity, but is instead distributed within a network. This distinguishes blockchain from traditional, centralized networks.
This decentralized system is also important because it promotes ownership without control, allowing everyone to use the platform freely. Decisions are made through consensus, where each transaction is approved by multiple nodes, rather than a single node.
Security
The security of a blockchain network can vary between different blockchains. In a public blockchain, validators or users use the internet to validate transactions and reach consensus. This makes public blockchains vulnerable to hacker attacks. Therefore, security is a crucial aspect for every blockchain.
Scalability
A blockchain network must have good scalability, meaning it can process a large number of user transactions quickly without increasing transaction costs. Scalability is important for mass adoption. If a blockchain has slow transaction processing speeds, people will be reluctant to use it.
How Does the Blockchain Trilemma Occur?
Currently, blockchains cannot optimize decentralization, security, and scalability simultaneously due to technological limitations. With the existing technology, development teams inevitably have to sacrifice one aspect. This leads to the blockchain trilemma.
If a blockchain wants to have optimal security and scalability, it will weaken decentralization as control is held by fewer entities. Conversely, prioritizing decentralization and security sacrifices scalability because distributed control slows transaction processing. Prioritizing decentralization and scalability weakens security since fewer participants make the blockchain more vulnerable to attacks.
Bitcoin’s blockchain is an example of how the blockchain trilemma occurs. Bitcoin prioritizes decentralization, with no central authority, and high security that makes it nearly impossible to hack. Bitcoin ensures security through cryptography and the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. With PoW, more participants in the network increase security.
However, to maximize these two aspects, Bitcoin sacrifices scalability. In a decentralized network, every transaction must be processed by all participants via PoW, which is not instantaneous. As a result, Bitcoin can only process 7 transactions per second compared to centralized networks like Visa that can process 63,000 transactions per second.
Solutions to the Blockchain Trilemma
Despite facing the blockchain trilemma, development teams are continually seeking solutions. So far, no definitive solution exists, but several approaches aim to address the trilemma:
Layer-1
In decentralized ecosystems, Layer-1 refers to blockchain protocols like Bitcoin, Litecoin, and Ethereum. Various methods are being developed to directly improve the scalability of Layer-1 blockchain networks.
Changing Consensus Mechanisms
The PoW mechanism is one of the most secure protocols but has slow transaction processing capacity. Blockchains like Bitcoin, Litecoin, and Ethereum use PoW. However, Ethereum recently transitioned from PoW to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) to improve scalability.
Instead of relying on miners for transaction verification, PoS asks validators to lock their crypto assets to secure the network and verify transactions. This mechanism speeds up transaction processing. Other consensus protocols include Solana’s Proof-of-History (PoH).
Sharding
Sharding is a blockchain architecture that allows each node (computer/server) processing verification to store only a small portion of the platform’s data. Through sharding, the data storage process is divided into smaller fragments (shards), which can then be distributed across different entities. Simultaneously, this process distributes the computational and data storage load across multiple nodes, thereby reducing the overall burden.
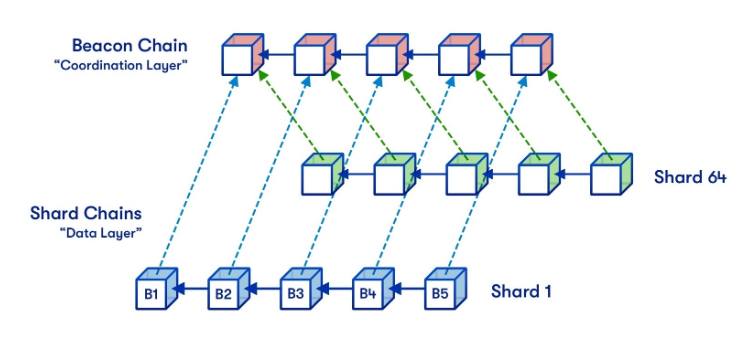
By dividing data storage into smaller fragments, sharding can improve scalability. Source: Vitalik Blog
As a result, sharding can increase network speed and scalability without sacrificing security and decentralization. One of the blockchains that implements sharding to improve scalability is Near Protocol. Through The Merge, Ethereum is now also utilizing sharding technology.
Here is the difference between Layer-1 and Layer-2:
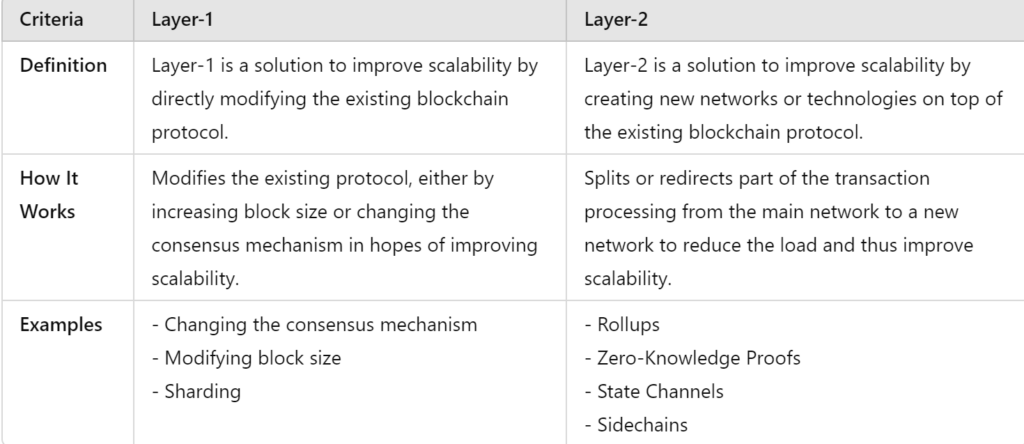
Layer-2
Layer-2 refers to networks or technologies that operate on top of existing blockchain protocols to improve scalability and efficiency of the underlying blockchain (Layer-1). Layer-2 solutions are increasingly popular for addressing scalability issues, especially for PoW consensus.
Rollups
Rollups are the most commonly used layer-2 solution to improve scalability. Rollups work by combining multiple layer-2 transactions and then submitting them as a single transaction to the main blockchain. This system uses validity proofs to ensure the integrity of a transaction.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Zero-Knowledge is an advanced cryptographic method that allows proof that a party knows or possesses certain data without having to disclose the entire information as evidence. The use of ZK can help blockchain enhance scalability while maintaining security. This is because ZK technology can verify transactions more quickly by only requiring ZK proof (zero-knowledge proof) instead of processing the entire data.
Since the entire data does not need to be processed, this also helps protect the privacy of data owners. Polygon is one of the blockchains actively developing and implementing ZK proof systems in its network. Additionally, several other crypto projects looking to adopt ZK technology include StarkNet, StarkEx, and zkSync.
State Channels
Instead of processing transactions on the main blockchain, state channels provide an additional layer to process transactions. State channels operate through a smart contract. So, when a transaction is made, its processing continues within the “channel,” meaning off the main blockchain, until it is completed. Once finalized, only the initial and final information is sent to the main blockchain for verification, rather than the entire transaction data. One example of a state channel is Bitcoin’s Lightning Network.
Sidechains
Sidechains are a combination of state channels and nested blockchains. They connect layer-1 with the main blockchain through a bridge that has its own consensus mechanism. This reduces the burden on the main blockchain for transaction validation. Typically, sidechains are used for a large number of transactions. An example is the largest blockchain-based game, Axie Infinity, which connects its Ronin sidechain to Ethereum.
Can the Blockchain Trilemma Be Solved?
Currently, there is no definitive solution to the blockchain trilemma. Existing technology does not allow developers to simultaneously optimize decentralization, security, and scalability. When technology advances to maximize transaction speeds without sacrificing decentralization and security, the blockchain trilemma will be resolved.
Meanwhile, Layer-1 and Layer-2 solutions and other efforts are the best ways to optimize blockchain capabilities. Developers continue to strive and remain optimistic about solving the blockchain trilemma, so we should also trust and be optimistic about its resolution in the future.
Start Investing with SafuBit
With SafuBit, you can securely and easily invest in a wide range of crypto assets, including BTC, BNB, ETH, and many more.
Why Choose SafuBit?
✔ Safe & Secure – Your transactions are protected with top-tier security protocols.
✔ Seamless Integration – Compatible with popular digital wallets like Metamask for effortless transactions.
✔ User-Friendly Platform – Buy, sell, and manage your crypto assets with ease.
💡 Stay Informed with SafuBit Academy
Learn more knowledge of crypto through various articles on Safubit Academy. All articles on Safubit Academy are created for educational and informational purposes only and are not intended as financial advice.
Don’t forget to follow our social media:
X : https://x.com/safubit
Medium : https://medium.com/@safubit.exchange


 February 10, 2025
February 10, 2025