
Layer 2 Crypto Unleashed: Faster, Cheaper & More Powerful!

Ethereum is the most widely used blockchain in the crypto industry. It was also the first blockchain to utilize smart contract technology, leading to the emergence of the NFT and DeFi sectors. As Ethereum’s user base has grown, its network weaknesses have become more apparent. Ethereum lacks high scalability, and network congestion has caused transaction gas fees to reach hundreds of US dollars. Consequently, Layer 2 technology was developed to address scalability issues and high transaction costs. So, what is Layer 2 crypto? How does it solve Ethereum’s scalability problems? This article will provide a comprehensive discussion of Layer 2 crypto on the Ethereum network.
Article Summary
⚖️ Layer 2 (L2) is a blockchain built on top of Layer 1 blockchain to address network scalability issues. The functions of Layer 2 include speeding up transaction processes, reducing transaction costs, and expanding the network’s use cases.
🧠 The most popular scaling method in the L2 sector is rollups, which bundle a group of transactions into a single piece of data that can be easily processed by Layer 1. In rollups, there are two popular implementations: Optimistic Rollup and Zero-Knowledge Rollup.
🚧 Some L2 projects using Optimistic Rollup include Arbitrum, Optimism, and Boba Network.
🏛️ L2 projects using ZK include Loopring, Immutable X, and Aztec Network. Additionally, several crypto projects are developing ZK technologies, such as Polygon, zkSync, STARKex, and STARKnet.
What Is Layer 2?
Layer 2 (L2) is a separate blockchain built on top of Layer 1 blockchain to address network scalability issues. Layer 2 technology was developed on the Ethereum network due to increasing Ethereum transaction costs and slow transaction processes (Ethereum transaction fees once reached $190). Thus, Layer 2’s functions are to speed up transaction processes, reduce transaction costs, and expand the network’s use cases. The presence of Layer 2 also alleviates the congestion on Layer 1, as network users are naturally distributed.
One significant advantage of Layer 2 is that it still leverages the consensus mechanism and security of the underlying Layer 1. Therefore, Layer 2 blockchains built on Ethereum benefit from the high-level security provided by Ethereum. This is one of the main reasons why Ethereum’s Layer 2 sector is very popular.
Developers recognize that the demand for applications on Ethereum remains high and Ethereum cannot meet this demand. This has accelerated the development of Layer 2 solutions. Currently, the L2 sector features various technologies addressing different transaction needs, such as DeFi, NFT, and crypto-based games. Some examples of L2 crypto projects include Polygon, Arbitrum, Loopring, Immutable X, and Optimism.
Advantages of Layer 2
⚡ Transaction Speed and Costs: Layer 2 blockchains are designed to have better transaction speed and lower costs compared to Layer 1. Some Layer 2 solutions on Ethereum even have transaction fees that are 10x cheaper than Ethereum.
🔒 Layer 1 Security: As explained earlier, the main advantage of Layer 2 is that it maintains the security of Layer 1. This is why Layer 2 has many more users compared to many other Layer 1 solutions.
🧠 Broader Use Cases: With faster transactions and much lower costs, Layer 2 opens up new use cases. Applications that were previously constrained by Ethereum’s network congestion (like trading apps such as GMX) can now choose to build on Layer 2 to meet their needs.
How Layer 2 Works
Layer 2 blockchains operate in parallel and extend Layer 1. There are two main ways Layer 2 processes transactions: either by processing them off-chain first and then returning them to Layer 1 or by performing everything on-chain using complex cryptographic techniques. This way, the most intensive work is handled by Layer 2, so Layer 1 only plays a role in the final validation stage.
The essence of this process is that Layer 2 continues to utilize the security provided by Ethereum without using its congested network verification processes. Layer 2 allows Layer 1 to handle security, data availability, and decentralization, while Layer 2 manages transaction scaling. Ethereum openly supports the development of Layer 2 as a scalability solution that does not compromise network decentralization and security.
Each Layer 2’s transaction processing methods vary and can be categorized into several types. Currently, the most popular method in L2 is rollup, which gathers multiple transactions and processes them off-chain. The batch of transactions is then sent back to Ethereum as a single piece of data that can be quickly processed. Among rollup methods, there are two variations: Optimistic Rollup and Zero-Knowledge (ZK).
Optimistic Rollup
How Optimistic Rollup Works. Source: ChainStack.
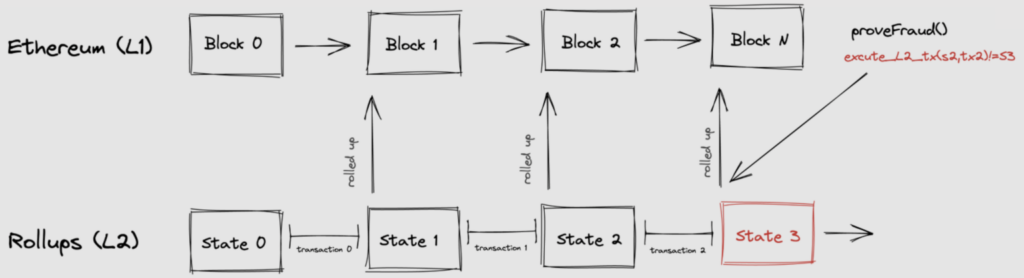
Optimistic Rollup is a Layer 2 technology that rolls up transactions into a single piece of data to be processed by Layer 1, like Ethereum. The rollup process occurs off-chain within each Layer 2 network, operating in parallel with Layer 1. Each Optimistic Rollup uses fraud proofs to check each batch of transactions for errors or potential risks.
All transactions entering a rollup are assumed to be valid (which is why it is called “optimistic”). Fraud proofs have a dispute time delay (DTD) of 7 days to review transactions for potential issues. Fraud proofs can be uploaded to the network during the DTD if a transaction is deemed invalid or risky. Additionally, fraud proofs do not disrupt network operations because they operate on top of the EVM and can be resolved quickly.
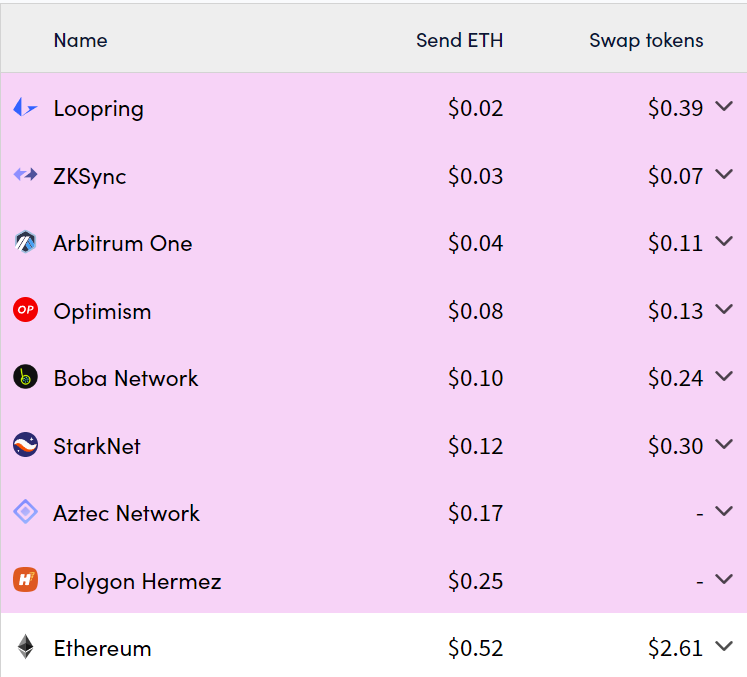
Comparison of Ethereum transaction fees with several Layer 2 projects.
Optimistic Rollup saves on transaction costs and speeds up transaction validation by compressing hundreds of transactions into a single piece of data. The rollup process avoids Ethereum network congestion by utilizing an off-chain network. As shown in the image above, L2s using Optimistic Rollup (such as Optimism and Arbitrum) can have transaction fees that are 10x cheaper than Ethereum.
However, a significant drawback of Optimistic Rollup is the time required to withdraw funds from the blockchain. This is related to the 7-day DTD of the fraud proof, which must verify transactions before successful withdrawal. Arbitrum and Optimism can take up to a week before users can withdraw their funds from the network.
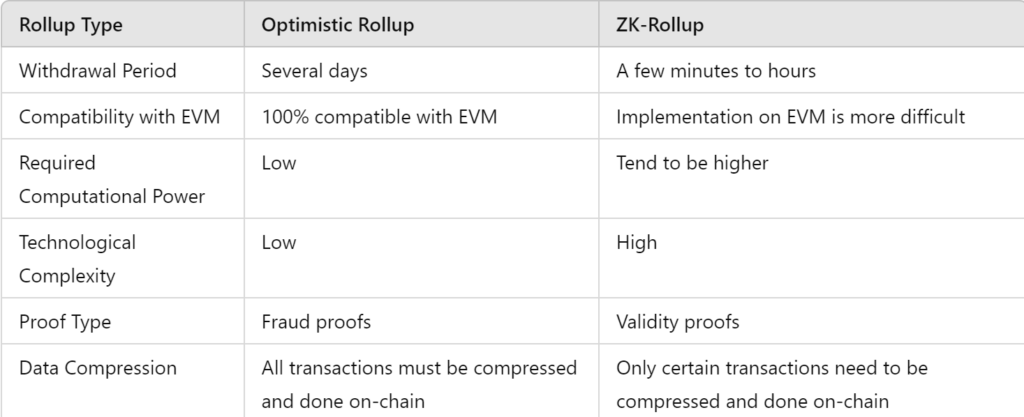
The table below compares Optimistic Rollup and zk-Rollup:
Zero-Knowledge
Zero-Knowledge (ZK) is the latest Ethereum scalability technology that uses validity proofs (zk-proofs) to ensure a batch of transactions is secure. The fundamental concept of ZK is similar to rollups, i.e., collecting several transactions into a piece of data that can be validated by the network. However, ZK can maintain the privacy of all transactions while still validating their correctness. Unlike Optimistic Rollup, ZK technology allows withdrawals to occur within minutes.
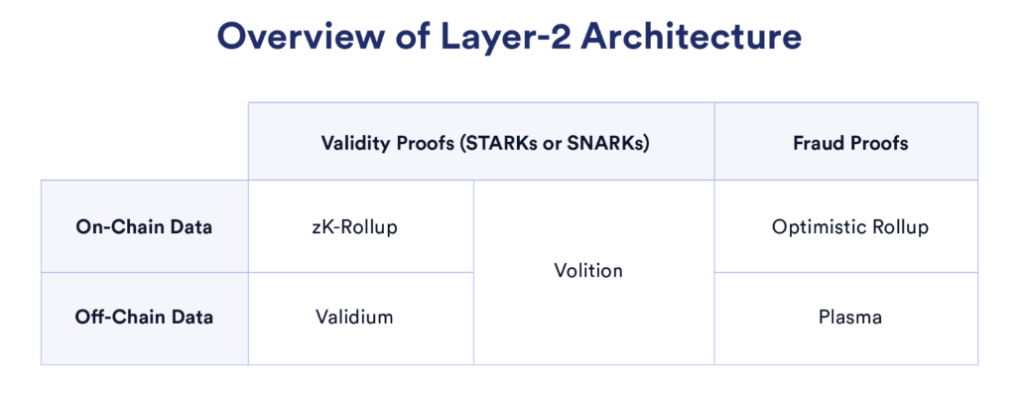
Layer 2 architecture based on proof type. Source: Chainlink Blog
The magic of this technology lies in zk-proofs (ZKP), which can prove the validity of transactions without exposing the private data within. There are two elements in generating ZKP: the verifier and the prover. The process of generating ZKP involves complex cryptographic operations and requires high computational power.
Additionally, ZK technology as an L2 Ethereum solution has several variations based on the type of ZKP created (interactive and non-interactive). Interactive ZKP requires the prover to prove the transaction’s validity to multiple verifiers, while non-interactive ZKP generates proofs that can be verified by all verifiers of the transaction.
There are two types of ZKP: zk-SNARK (succinct non-interactive argument of knowledge) and zk-STARK (scalable transparent argument of knowledge). zk-STARK is more secure, scalable, and transparent compared to zk-SNARK. However, zk-STARK requires larger ZKP sizes and longer verification times. zk-SNARK is more gas-efficient and faster. Currently, various zk project teams are working on reducing the complexity of generating ZKP.
Other Layer 2 Methods
Sidechain: A sidechain is an L2 solution in the form of an independent blockchain that runs parallel to the main Ethereum network. It is compatible with the EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) but must use bridge technology to interact with Ethereum. Therefore, sidechains cannot benefit from the security provided by Ethereum.
Validium and Volition: Validium is a zk technology that uses an off-chain system to store data, thereby reducing gas costs and increasing TPS (transactions per second). Like sidechains, Validium does not utilize the security offered by L1. Meanwhile, Volition allows users to choose between using zk-rollup or Validium.
Some Layer 2 Projects
Polygon
Polygon (MATIC) is one of the most popular Ethereum L2 projects. The main L2 of Polygon currently is Polygon PoS, a unique sidechain that has its own consensus mechanism but still leverages some security features of Ethereum. Polygon PoS has processed 960 million transactions and has 200 million users based on total unique addresses. Polygon is also developing 4 other layer 2 solutions, 3 of which use ZK technology.
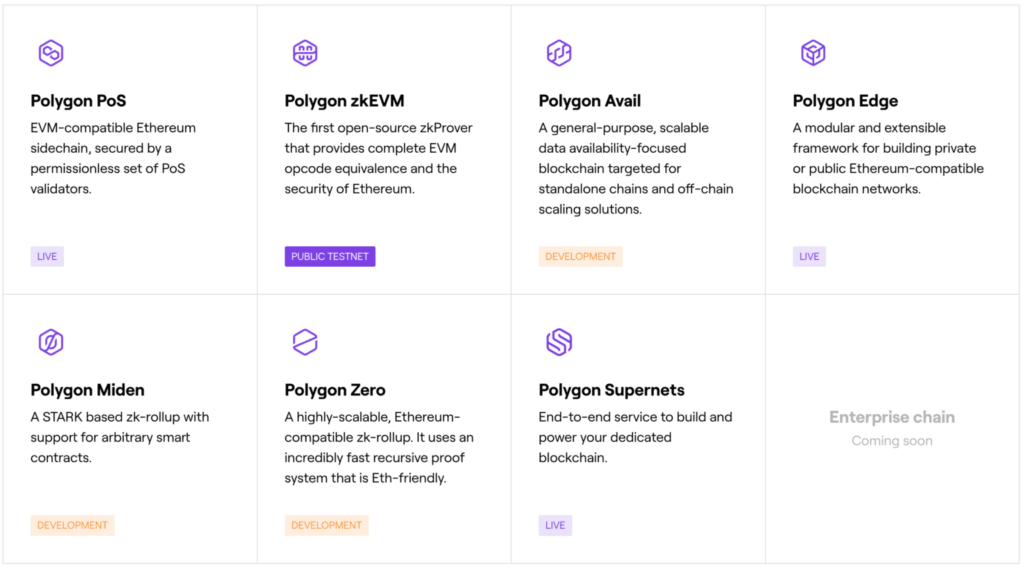
L2 product currently being developed by Polygon. Source: Polygon
As shown in the image above, there are 5 L2 solutions within the Polygon ecosystem: Polygon PoS, zkEVM, Avail, Zero, and Miden. Polygon zkEVM, Zero, and Miden represent Polygon’s efforts to enter the popular ZK sector. Among these three zk projects, zkEVM is touted to have the greatest potential. Polygon zkEVM is the only zk layer 2 that has direct compatibility with the EVM.
Additionally, Polygon has successfully attracted various major brands to use its L2 platform. Some of these include Robinhood, which aims to create a Web3 wallet, Starbucks’ NFT platform, and collaborations with Meta.
Applications built on Polygon: AAVE, OpenSea, UniSwap v3, Curve, Balancer, and Benji Bananas.
Optimism
Optimism (OP) is an Ethereum L2 project established in 2019. It utilizes optimistic rollup technology to reduce transaction costs and speed up the process. As previously explained, Optimistic Rollup can leverage Ethereum’s state-of-the-art security without facing its network congestion. Optimism’s transaction costs are almost 90% cheaper than Ethereum. Optimism has the 3rd largest TVL (total value locked) after Polygon and Arbitrum. This is also reflected in daily transaction data and active wallet addresses.
Applications built on Optimism: OpenSea, Velodrome, Synthetix, and AAVE v3.
Arbitrum
Arbitrum is a layer 2 crypto project developed by Offchain Labs and has been operational since 2021. Like Optimism, Arbitrum uses Optimistic Rollup technology, which rolls up transactions into a piece of data and processes them off-chain. This makes transactions on Arbitrum much faster and costs comparable to its competitors. As of January 27, 2023, Arbitrum has the second-largest TVL in the L2 sector at $1.17 billion.
Arbitrum also has two parallel L2s: Arbitrum One and Nova. One is the main Arbitrum chain using rollup technology, while Arbitrum Nova is an AnyTrust Chain. AnyTrust Chain has higher TPS and lower transaction costs but sacrifices decentralization. Arbitrum Nova is designed to meet the needs of developers requiring high TPS, such as for games or trading platforms.
In August 2022, Arbitrum completed its largest update, Arbitrum Nitro. With Nitro, Arbitrum’s TPS increased by 7-10 times, transaction costs became cheaper, and synchronization between Arbitrum and Ethereum improved. Nitro also updated ArbOS, Arbitrum’s execution engine or AVM (Arbitrum Virtual Machine). The reason Nitro is a significant update for Arbitrum is the integration of Geth into the AVM. This ensures that transactions and contracts on Arbitrum are automatically consistent and aligned with Ethereum.
Applications built on Arbitrum: GMX, OpenSea, Curve, UniSwap V3, and TreasureDAO.
zk Projects
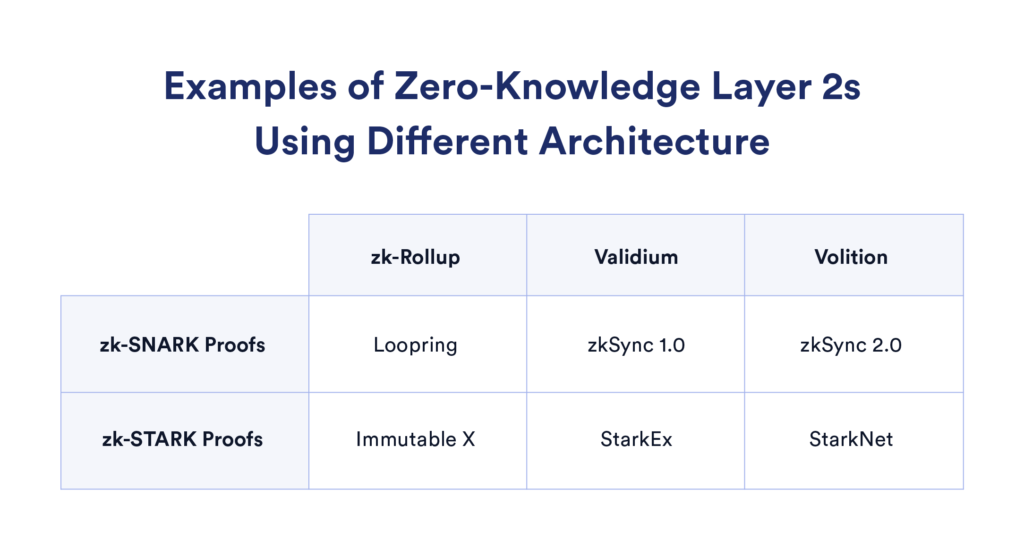
Implementation of ZK technology. Source: Chainlink Blog.
ZK projects gained a lot of attention in 2022. Some crypto projects like dYdX, Loopring, and Immutable X have successfully implemented ZK technology in their operations. Loopring and dYdX are decentralized trading platforms that can benefit from the high TPS of ZK technology. This year, many ZK projects are focusing on further developing ZK implementation, especially its compatibility with Ethereum. However, the higher complexity of ZK also poses a barrier to broader adoption of the technology.
As shown in the image above, ZK technology also has many variations, with different projects choosing various implementations. Polygon’s ZK projects focus on using zk-STARKs, while platforms like Loopring use zk-SNARKs.
Additionally, zkEVM projects are crucial because zk technology currently lacks compatibility with EVM. Currently, there are three crypto projects developing zkEVM: Polygon, Scroll, and zkSync. The implementation of zkEVM could be a significant milestone in advancing zk adoption on Ethereum.
Buying Cryptocurrency on SafuBit
You can start investing in crypto assets easily and securely on SafuBit. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to buy crypto using the SafuBit platform:
How to Buy Crypto on SafuBit
1️⃣ Create a SafuBit Account
- Sign up on SafuBit.com and complete the identity verification process to begin trading.
2️⃣ Deposit Funds
- On the homepage, click the Deposit button and add funds using your preferred payment method.
3️⃣ Search for Your Favorite Coin
- Open the Market page and look for the crypto asset you want to buy.
4️⃣ Buy Crypto
- Click Buy, enter the desired amount, and confirm your purchase.
✅ Now you own crypto assets!
Why Choose SafuBit?
✔ Secure & Regulated
- SafuBit ensures top-tier security and complies with global regulatory standards.
✔ Seamless Transactions
- The platform supports fast and easy crypto purchases with multiple payment options.
✔ Metamask & Web3 Integration
- SafuBit is compatible with popular digital wallets like Metamask, making transactions even more convenient.
✔ Learn & Stay Updated
- Explore educational content on SafuBit Academy, where you can access the latest insights on crypto and blockchain technology.
Learn more knowledge of crypto through various articles on Safubit Academy. All articles on Safubit Academy are created for educational and informational purposes only and are not intended as financial advice.
Don’t forget to follow our social media:
X : https://x.com/safubit
Medium : https://medium.com/@safubit.exchange


 February 10, 2025
February 10, 2025